
The equation of motion:

This equation guarantees that trajectories don't intersect.
A separable Hamiltonian
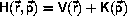
A dynamics is invertible, left, if any point in
phasespace is the image of a single
point in phasespace.
The dynamics is non-invertible, right, if the motion transforms two different
points into a single point in phasespace.

Time-reversal symmetry causes microscopic reversibility, wrs = wsr.
Author Per Stoltze stoltze@fysik.dtu.dk