


Next: About this document
Physics 110: Practice Final Exam
- 1.
- A binary star system has an orbital period of 1 year. It is most likely that this system would be observed to be
- (a)
- a visual binary.
- (b)
- a spectroscopic binary.
- (c)
- an eclipsing binary.
- (d)
- a wide binary.
- (e)
- a close binary.
- 2.
- In a certain eclipsing binary system, primary minimum occurs when star X is eclipsed by star Y. What can we say about the temperatures of the two stars?
- (a)
- star X is hotter than star Y.
- (b)
- star X is cooler than star Y.
- (c)
- stars X and Y are the same temperature.
- (d)
- not enough information given, need to know the size of each star.
- (e)
- not enough information given, need to know the luminosity of each star.
- 3.
- Mass exchange in close binary systems can produce
- (a)
- X-ray emission from an accretion disk.
- (b)
- recurrent novae if one partner is a white dwarf.
- (c)
- modification of the evolutionary status of both stars.
- (d)
- some (but not all) of the three responses is correct.
- (e)
- all of the three responses is correct.
- 4.
- Observations of a binary star system show that the orbital period is increasing. Astronomers conclude that
- (a)
- the more massive star is transferring matter to the less massive star.
- (b)
- the less massive star is transferring matter to the more massive star.
- (c)
- both stars are gaining mass from the interstellar medium.
- (d)
- one of the stars is going to explode as a type Ia supernova.
- (e)
- one of the stars is a compact object (a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole).
- 5.
- The explosive burning of hydrogen on the surface of a white dwarf produces
- (a)
- a type Ia supernova.
- (b)
- a pulsar.
- (c)
- an X-ray burster.
- (d)
- a nova.
- (e)
- a millisecond pulsar.
- 6.
- When a black hole is part of a close binary star system, the system may be a strong source of X-rays. Where do the X-rays come from?
- (a)
- the companion star, which is heated by the black hole.
- (b)
- from the black hole itself.
- (c)
- from planets which are captured by the black hole.
- (d)
- from infalling matter that heats up when it strikes the black hole at the Schwarzschild radius.
- (e)
- a disk of hot matter around the black hole.
- 7.
- The 21-centimeter line of atomic hydrogen
- (a)
- is strongly absorbed by dust.
- (b)
- provides the ONLY evidence that our Sun orbits the center of the Galaxy.
- (c)
- is emitted primarily by the hot gas in the dark halo of our Galaxy.
- (d)
- has been only rarely observed by radio astronomers.
- (e)
- is our best tool for mapping the structure and rotation of our Galaxy.
- 8.
- The hydrogen in an H II region is mostly
- (a)
- in molecular form.
- (b)
- ionized.
- (c)
- neutral.
- (d)
- excited.
- (e)
- tied up in dust particles.
- 9.
- What kind of object creates an evacuated, very hot bubble in the interstellar gas?
- (a)
- a red giant star.
- (b)
- a black hole.
- (c)
- a supernova.
- (d)
- a globular cluster.
- (e)
- a reflection nebula.
- 10.
- When our Galaxy is mapped using star counts, absorption by dust makes the Galaxy appear
- (a)
- smaller than it actually is.
- (b)
- younger than it actually is.
- (c)
- flatter than it actually is.
- (d)
- older than it actually is.
- (e)
- dirtier than it actually is.
- 11.
- What did Harlow Shapley discover about the globular clusters that allowed him to determine the size of the Galaxy and the Sun's location within it?
- (a)
- the clusters are confined to a thin plane.
- (b)
- the clusters are all located at the same distance from the Sun.
- (c)
- the center of the distribution of clusters is far from the Sun.
- (d)
- all of the clusters are located in a region a few parsecs across.
- (e)
- the clusters are expanding away from the Galactic center.
- 12.
- Which of the following properties does NOT apply to the disk of the Milky Way?
- (a)
- The stars have a wide range of ages.
- (b)
- There is a great deal of gas.
- (c)
- There is a great deal of dust
- (d)
- There is evidence for spiral arms.
- (e)
- The stars move in random directions.
- 13.
- What is the main evidence for dark matter in the Milky Way?
- (a)
- A rotation curve that stays flat beyond the visible edge.
- (b)
- That stars are forming in spiral arms.
- (c)
- That many stars have planets.
- (d)
- There are more pulsars than we can observe directly.
- (e)
- The globular clusters are concentrated towards the center.
- 14.
- Which of the following are possible candidates for the dark matter in our Galaxy?
- (a)
- normal stars, dust, black holes.
- (b)
- normal stars, Jupiter-like planets, snowballs.
- (c)
- unknown elementary particles, brown dwarfs, neutron stars.
- (d)
- dust, Jupiter-like planets, brown dwarfs.
- (e)
- dust, gas, normal stars.
- 15.
- Which of the following combinations of information about the Sun and its orbit within the Galaxy could be used to determine the amount of galactic mass that lies within the Sun's orbit?
- (a)
- distance from the center and orbital period.
- (b)
- Sun's mass and orbital speed.
- (c)
- distance from the center and age.
- (d)
- Sun's mass and age.
- (e)
- Sun's mass and distance from the center.
- 16.
- The spiral arms of a galaxy are believed to
- (a)
- be composed of the same stars all the time.
- (b)
- be a density wave pattern.
- (c)
- be regions where there is less obscuring dust.
- (d)
- have appeared very recently.
- (e)
- be part of the galaxy's halo.
- 17.
- Halo stars
- (a)
- are mostly very young.
- (b)
- are mostly quite old.
- (c)
- have a wide mixture of ages.
- (d)
- are forming rapidly from gas and dust.
- (e)
- are mostly O and B type stars.
- 18.
- Which of the following best describes the way that our Galaxy has evolved during its lifetime?
- (a)
- it has grown flatter and richer in heavy elements.
- (b)
- it has grown less flattened and richer in heavy elements.
- (c)
- it has grown flatter and poorer in heavy elements.
- (d)
- it has grown less flattened and poorer in heavy elements.
- (e)
- it has remained essentially unchanged.
- 19.
- Which of the following properties is NOT relevant to the classification of galaxies into their different Hubble types?
- (a)
- Degree of winding of the spiral arms.
- (b)
- Prominence of the central bulge.
- (c)
- Overall shape.
- (d)
- Existence of dust and young stars.
- (e)
- The number of Cepheid variable stars.
- 20.
- Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of elliptical galaxies?
- (a)
- ellipsoidal shape
- (b)
- no cool gas
- (c)
- no present-day star formation
- (d)
- a smooth distribution of light
- (e)
- a disk
- 21.
- One primary difference between spiral and elliptical galaxies is
- (a)
- all ellipticals are more massive than spirals.
- (b)
- ellipticals contain less interstellar matter than spirals do.
- (c)
- star formation is more common in ellipticals than spirals.
- (d)
- spirals have more stars than do ellipticals.
- (e)
- ellipticals can have bars, but spirals cannot.
- 22.
- Suppose a galaxy has a flat rotation curve. How does the amount of mass within 20 kpc compare to the amount of mass within 10 kpc?
- (a)
- twice as much.
- (b)
- four times as much.
- (c)
- half as much.
- (d)
- one-quarter as much.
- (e)
- can't tell, not enough information given.
- 23.
- The ``spiral nebulae'' were not at first recognized as external galaxies similar to the Milky Way because
- (a)
- nobody was at all interested in them.
- (b)
- we could not identify the lines in their spectra.
- (c)
- we did not know a distance to any of them.
- (d)
- the Catholic Church opposed the idea.
- (e)
- they were thought to be comets.
- 24.
- Which of the following statements regarding galaxy formation is FALSE?
- (a)
- Ellipticals are the most common galaxy type in high density environments.
- (b)
- Galaxy collisions are relatively common.
- (c)
- Elliptical galaxies need to shed angular momentum as they form.
- (d)
- Galaxies formed relatively early in the history of the universe.
- (e)
- Galaxies formed as ellipticals; afterwards some then developed into spirals.
- 25.
- Cepheid variables can be used directly to measure distances
- (a)
- only within our own galaxy.
- (b)
- to only the nearest galaxies (within a few megaparsecs).
- (c)
- only to dwarf galaxies.
- (d)
- only to galaxies in clusters.
- (e)
- to all galaxies that we can detect.
- 26.
- Consider the maximum distance to which a distance indicator in astronomy can be reliably used. Which of the following lists objects or techniques in increasing order of this maximum reliable distance?
- (a)
- parallax, Cepheids, supernovae.
- (b)
- parallax, supernovae, Cepheids.
- (c)
- Cepheids, parallax, supernovae.
- (d)
- parallax, Tully-Fisher relation, Cepheids.
- (e)
- Cepheids, Tully-Fisher relation, novas.
- 27.
- Hubble's constant is still not known accurately today because it is
- (a)
- changing all the time.
- (b)
- hard to measure accurate colors of galaxies.
- (c)
- hard to measure accurate recession speeds of galaxies.
- (d)
- hard to measure accurate distances to galaxies.
- (e)
- hard to measure transverse speeds of galaxies.
- 28.
- A galaxy at a distance of 200 megaparsecs is moving away from us at 20,000 km/s. About how far away is another galaxy with a recession speed of 10,000 km/s?
- (a)
- 50 megaparsecs
- (b)
- 400 megaparsecs
- (c)
- 100 megaparsecs
- (d)
- 800 megaparsecs
- (e)
- not enough information given.
- 29.
- What are quasars?
- (a)
- The structures in the universe with the largest size and greatest mass.
- (b)
- The distortion of the path of a ray of light, caused by very dense masses.
- (c)
- An ancient exploding star, sometimes seen in our own galaxy.
- (d)
- Intense sources of energy in the centers of very distant galaxies.
- (e)
- A brand of television set produced by Motorola.
- 30.
- Which of the following was NOT a property of the first quasars to be discovered?
- (a)
- a strong radio source
- (b)
- a star-like appearance at optical wavelengths
- (c)
- an unusually high redshift
- (d)
- broad emission lines
- (e)
- a high proper motion
- 31.
- The evidence that the central engine of a quasar is small is that it
- (a)
- contains a black hole.
- (b)
- appears to be a point source of light.
- (c)
- has broad emission lines in the spectrum.
- (d)
- can vary in brightness by large factors in a short time.
- (e)
- has a large redshift.
- 32.
- Superluminal motion requires that matter ejected by an active galactic nuclei
- (a)
- travel faster than the speed of light.
- (b)
- have a high proper motion.
- (c)
- be coming from a jet that is nearly aligned with our viewing direction.
- (d)
- be hot and highly ionized.
- (e)
- be highly redshifted.
- 33.
- Which of the following is NOT a general property of the nuclei of Seyfert galaxies?
- (a)
- The nucleus has a steady brightness.
- (b)
- The nucleus has a non-thermal spectrum.
- (c)
- The spectral emission lines are very broad.
- (d)
- The nucleus is often bright in the infrared.
- (e)
- The nucleus often emits strong radio signals.
- 34.
- The nucleus of an active galaxy is thought to be powered by
- (a)
- a single very massive star.
- (b)
- an unusually long-lived supernova.
- (c)
- an accretion disk around a black hole.
- (d)
- the latest jet engine from Pratt & Whitney.
- (e)
- the force of a whole galaxy.
- 35.
- Which of the following statements about the Local Group is TRUE?
- (a)
- the Milky Way is the only large spiral galaxy in the Local Group.
- (b)
- the Virgo cluster is part of the Local Group.
- (c)
- the galaxies in the Local Group are all rushing toward the Milky Way.
- (d)
- it contains a few dozen galaxies.
- (e)
- their latest rock video is awesome.
- 36.
- There is often a giant, dominant elliptical at the center of galaxy clusters. It is thought to arise from
- (a)
- a collection of black holes at the center.
- (b)
- large amounts of hydrogen gas collecting in the core.
- (c)
- gravitational effects of the local supercluster.
- (d)
- tidal interactions among members of the cluster.
- (e)
- radio jets accreting matter.
- 37.
- Why do we believe that most of the mass in galaxy clusters is dark?
- (a)
- Clusters would quickly disperse if they contained only the luminous matter.
- (b)
- Galaxy clusters are all far away.
- (c)
- Galaxy clusters are strong sources of neutrinos.
- (d)
- There is very little gas in galaxy clusters.
- (e)
- The galaxies are heavily obscured by dust.
- 38.
- Which of the following is the principal problem with the pancake model for cluster formation?
- (a)
- clusters are forming at the present epoch, in conflict with observations.
- (b)
- there is no explanation for voids in the galaxy distribution.
- (c)
- it cannot explain why galaxy clusters appear to be round, rather than flattened.
- (d)
- the primordial gas clouds cannot collapse because of angular momentum conservation.
- (e)
- galaxies form too late in this scenario.
- 39.
- Which of the following best describes the distribution of galaxies in the nearby universe?
- (a)
- Galaxies lie on sheets and chains surrounding empty regions.
- (b)
- Galaxies are distributed uniformly in space.
- (c)
- There are a few large clusters of galaxies with nothing in between.
- (d)
- There are many clusters of galaxies near us in space, but nothing beyond.
- (e)
- All galaxies go around in pairs.
- 40.
- The statement that the universe is isotropic means that it
- (a)
- appears the same, no matter at what time it is observed.
- (b)
- appears the same in all directions, no matter where the observer is located.
- (c)
- appears the same in all directions only when viewed from the expansion center.
- (d)
- began in an explosive event of extreme temperature and density.
- (e)
- consists of a four-dimensional space-time continuum.
- 41.
- The night sky is dark because
- (a)
- the universe is not uniform.
- (b)
- the universe is not isotropic.
- (c)
- the universe is not eternal.
- (d)
- the universe is filled with dust.
- (e)
- distant stars are fainter by the inverse square law.
- 42.
- An observer now located at a distance of 3 billion light years from us could look in our general direction and see
- (a)
- most of the galaxies approaching him or her.
- (b)
- the same Hubble's Law that we see.
- (c)
- about equal numbers of red and blue shifted galaxies.
- (d)
- everything rushing away from a point near the Milky Way galaxy.
- (e)
- generally blue shifted galaxies in the direction toward the Milky Way galaxy and generally red shifted galaxies in the opposite direction.
- 43.
- Astronomers believe that the age of the Universe is about
- (a)
- 15,000,000 (15 million) years
- (b)
- 150,000 years
- (c)
- 1,500,000 years
- (d)
- 15,000 years
- (e)
- 15,000,000,000 (15 billion) years
- 44.
- Tomorrow a group of astronomers will announce that the value of
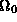 is exactly equal to one. Based on this, which of the following statements is TRUE?
is exactly equal to one. Based on this, which of the following statements is TRUE?
- (a)
- The steady state theory will need to be revived as an alternative to the Big Bang theory.
- (b)
- The theory of inflation is dealt a serious, and perhaps, fatal blow.
- (c)
- The expansion of the Universe will eventually stop and recollapse.
- (d)
- The Universe will expand forever.
- (e)
- The Nobel Prize will be awarded to an astronomer this year.
- 45.
- What observations could, in principle, determine whether the universe is open or closed?
- (a)
- Measuring the redshifts of a large number of quasars.
- (b)
- Measuring the precise temperature of the microwave background.
- (c)
- Comparing the value of the Hubble constant at early times with its current value.
- (d)
- Measuring the abundance of hydrogen in the interstellar medium of our Galaxy.
- (e)
- None - this question cannot be resolved except by theoretical arguments.
- 46.
- How long after the Big Bang did the universe become transparent?
- (a)
- It has always been transparent.
- (b)
- About 3 minutes.
- (c)
- About 1 year.
- (d)
- A few hundred thousand years.
- (e)
- About 5 billion years.
- 47.
- The cosmic background radiation detected by Penzias & Wilson has a very low temperature because it
- (a)
- is emitted by nearby very cold gas.
- (b)
- has been redshifted from a much higher temperature earlier in the universe.
- (c)
- interferes only very slightly with telecommunications.
- (d)
- is redshifted by the motion of the Earth.
- (e)
- was observed at a very low frequency, and has a higher temperature at other frequencies.
- 48.
- We say that the early universe was radiation dominated because
- (a)
- no matter existed for the first few hours after the Big Bang.
- (b)
- dangerous forms of radiation produced many genetic mutations.
- (c)
- radiation was being created at a faster rate than it was being destroyed.
- (d)
- the energy density in radiation exceeded that in matter.
- (e)
- radiation density has decreased since then while the matter density has remained constant.
- 49.
- The density of ordinary matter in the early universe can be determined most precisely by measuring the present-day abundance of
- (a)
- helium
- (b)
- hydrogen
- (c)
- carbon
- (d)
- deuterium
- (e)
- iron
- 50.
- Abstract arguments about the possible existence of life elsewhere in the universe
- (a)
- conclusively prove that many other civilizations exist.
- (b)
- conclusively prove that no other civilizations could have developed.
- (c)
- are completely inconclusive.
- (d)
- are irrelevant because the existence of UFOs has been conclusively established.
- (e)
- are irrelevant because we have already detected radio signals from other civilizations.



Next: About this document
John Hughes
Tue Apr 6 12:05:54 EDT 1999