


Next: About this document
Physics 109: Practice Mid-term
- 1.
- It's late afternoon and the Sun is setting. You hold out
your arm and notice that the width of your fist across the knuckles is
equal to the height of the Sun above the horizon. Approximately how
much time is left before sunset?
- (a)
- 1 hour.
- (b)
- 20 minutes.
- (c)
- 80 minutes.
- (d)
- 40 minutes.
- (e)
- a half-hour.
- 2.
- The Large Magellanic Cloud is a nearby galaxy that is
approximately
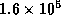 light years away;
light years away; 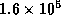 is
is
- (a)
- 1.6 million.
- (b)
- 16 thousand.
- (c)
- 160 thousand.
- (d)
- 1.6 billion.
- (e)
- 16 million.
- 3.
- The azimuth and altitude of an object located due south and
on the horizon are
- (a)
- azimuth 180
 , altitude 0
, altitude 0 
- (b)
- azimuth 90
 , altitude 90
, altitude 90 
- (c)
- azimuth 90
 , altitude 0
, altitude 0 
- (d)
- azimuth 0
 , altitude 180
, altitude 180 
- (e)
- azimuth 180
 , altitude 90
, altitude 90 
- 4.
- The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes:
- (a)
- the phases of the Moon.
- (b)
- diurnal motion of the stars.
- (c)
- retrograde motion of the planets.
- (d)
- the Sun to move through the zodiacal constellations.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 5.
- The point on the celestial sphere directly above your head is called
- (a)
- the pole.
- (b)
- the meridian.
- (c)
- the horizon.
- (d)
- the zenith.
- (e)
- the ecliptic.
- 6.
- Which of the following is NOT true of circumpolar
stars in the northern hemisphere:
- (a)
- they do not rise or set.
- (b)
- sometimes their motion is eastward.
- (c)
- they appear to move in counterclockwise circles.
- (d)
- sometimes their motion is westward.
- (e)
- they appear to move in clockwise circles.
- 7.
- The ecliptic is the
- (a)
- line that divides the celestial sphere into northern and
southern hemispheres.
- (b)
- apparent path of the Sun on the celestial sphere.
- (c)
- circle on the celestial sphere that defines the circumpolar
regions.
- (d)
- great circle located
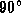 from the zenith.
from the zenith.
- (e)
- circle on the celestial sphere that passes through the
zenith and the celestial poles.
- 8.
- Which of the following is true?
- (a)
- A sidereal day is equal to a solar day on the Earth.
- (b)
- A sidereal day is about 4 minutes longer than a solar day
on the Earth.
- (c)
- A sidereal day is about 4 minutes shorter than a solar day
on the Earth.
- (d)
- A sidereal day is the same for all planets.
- (e)
- none of the other answers are true.
- 9.
- An astronaut on the Moon watches the Earth. When we see the
full moon, what phase of the Earth does the astronaut see?
- (a)
- new.
- (b)
- gibbous.
- (c)
- crescent.
- (d)
- full.
- (e)
- none, the Earth would be in eclipse.
- 10.
- Which of the following is true of the motion of the planet
Mars among the stars?
- (a)
- all retrograde loops have the same shape.
- (b)
- retrograde loops are always separated by the same interval
of time.
- (c)
- all retrograde loops occur in the same constellation.
- (d)
- retrograde loops occur when Mars is in conjunction.
- (e)
- Mars always moves eastward with respect to the stars.
- 11.
- The occurrence of seasons on the Earth is due to
- (a)
- the Earth being closer to the Sun in summer.
- (b)
- the Earth changing its rotation rate during the year.
- (c)
- the Earth's axis pointing in different directions during the year.
- (d)
- the Earth's axis being inclined to the ecliptic.
- (e)
- more clouds covering the Earth in winter and blocking the sunlight.
- 12.
- Eudoxus's model of the solar system would have required which
of the following to explain the motion of the Sun:
- (a)
- one sphere rotating westward once per day.
- (b)
- one sphere rotating eastward once per day.
- (c)
- one sphere rotating westward once per day, and another
rotating eastward once per year.
- (d)
- one sphere rotating eastward once per day, and another
rotating westward once per year.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 13.
- An object with an angular size of 1 degree moves three times
farther away. What is its new angular size?
- (a)
- 3 degrees
- (b)
- 20 minutes of arc
- (c)
- 3 minutes of arc
- (d)
- 33 seconds of arc
- (e)
- 33 minutes of arc
- 14.
- Which of the following is a reason that the ancient Greek
astronomers rejected Aristarchus' heliocentric model of the solar
system?
- (a)
- it did not account for the retrograde motions of the planets.
- (b)
- it could not explain the phases of Venus.
- (c)
- it used elliptical rather than circular orbits for the planets.
- (d)
- it could not account for the Coriolis effect.
- (e)
- it predicted stellar parallax which they could not detect.
- 15.
- Which of the following is FALSE?
- (a)
- Hipparchus made an accurate measurement of the distance to the Moon.
- (b)
- Aristarchus made a rough estimate of the size of the Sun.
- (c)
- Aristotle knew that the Moon orbits the Earth.
- (d)
- Pythagoras knew that the Earth is spherical.
- (e)
- Ptolemy believed that the Sun was the center of the universe.
- 16.
- Hipparchus discovered precession, which is
- (a)
- the slow motion of the Earth's rotation axis on the
celestial sphere.
- (b)
- the apparent backward motion of the stars from night to
night.
- (c)
- periodic reversals in the direction of the Earth's magnetic field.
- (d)
- the motion of the Sun relative to the Earth.
- (e)
- the motion of the planets during retrograde motion.
- 17.
- In Ptolemy's cosmology, the motion of a planet (other than
the Earth) could be described as
- (a)
- the planets revolved around the Sun in circular orbits.
- (b)
- the planets were fixed in space, unmoving.
- (c)
- planets moved on circles named epicycles, which in turn
moved on circles named deferents.
- (d)
- the planets moved on elliptical orbits centered on the equant.
- (e)
- The planets revolved around the Sun, which in turn revolved
around the Earth.
- 18.
- Why were epicycles used by Copernicus in his model of the
solar system?
- (a)
- To explain retrograde motion.
- (b)
- To account for regular deviations in the orbital speeds of
the planets.
- (c)
- To account for the changing brightnesses of the planets.
- (d)
- To explain the differences between the synodic and sidereal
periods of the planets.
- (e)
- So that the underlying orbits of the planets could be
elliptical.
- 19.
- One advantage of the Copernican model of the solar system
over the Ptolemaic one was:
- (a)
- it was a much better description of the observational
evidence then available.
- (b)
- it made use of fewer circles to describe the motions of the
planets.
- (c)
- it made use of elliptical orbits for the planets.
- (d)
- it eliminated the problem of not detecting stellar
parallax.
- (e)
- it provided a means to deduce the relative sizes of the
orbits of the planets.
- 20.
- Which of the following was a consequence of Tycho's failure
to detect stellar parallax?
- (a)
- it convinced him that Saturn was the outermost planet.
- (b)
- it convinced him that the stars are bigger than the solar
system.
- (c)
- it convinced him that the stars are very far away.
- (d)
- it convinced him that the Earth was stationary.
- (e)
- it was the reason he was fired by King Christian IV of
Denmark.
- 21.
- Suppose the distance between the two foci of an ellipse is
much smaller than the semimajor axis of the ellipse. What can be said
about the ellipse?
- (a)
- the eccentricity of the ellipse is nearly 0.
- (b)
- the eccentricity of the ellipse is nearly 1/2.
- (c)
- the eccentricity of the ellipse is nearly 1.
- (d)
- the eccentricity of the ellipse is undefined.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 22.
- Kepler's first law states that the Sun is located at one
focus of the orbit of a planet. What is at the other focus?
- (a)
- the Earth.
- (b)
- nothing.
- (c)
- the planet itself.
- (d)
- one of the other planets.
- (e)
- Elvis.
- 23.
- According to Kepler's second law, a planet moves fastest in
its orbit when it is at
- (a)
- perihelion.
- (b)
- aphelion.
- (c)
- elongation.
- (d)
- conjunction.
- (e)
- opposition.
- 24.
- If the size of the Earth's orbit were doubled, its period
of revolution about the Sun would
- (a)
- decrease about eight times.
- (b)
- decrease about three times.
- (c)
- increase about three times.
- (d)
- increase about eight times.
- (e)
- stay the same.
- 25.
- Which of the following did Galileo NOT observe with
his telescope?
- (a)
- the many stars that make up the Milky Way.
- (b)
- the moons of Jupiter.
- (c)
- mountains on the Moon.
- (d)
- a constant angular size for Mars.
- (e)
- sunspots.
- 26.
- What was the significance of Galileo's discovery that Venus
shows all phases from new to full?
- (a)
- it allowed him to find Venus' distance from the Sun.
- (b)
- it proved to other astronomers that his telescope was
working correctly.
- (c)
- in the geocentric model, only some phases are possible.
- (d)
- it proved that Venus has an atmosphere.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 27.
- Galileo's studies of the motions of objects (mechanics)
resulted in the following conclusion:
- (a)
- the natural state of an object was to be at rest.
- (b)
- the rate at which an object increased its speed while it
fell was the same for all objects.
- (c)
- the rate at which an object increased its speed while it
fell depended on the mass of the object.
- (d)
- the rate at which an object increased its speed while it
fell depended on the weight of the object.
- (e)
- the motion of an object could continue only as long as a
force was at work.
- 28.
- The concept of inertial motion states that, in the absence of
an unbalanced force, an object may
- (a)
- move at a constant speed in a straight line.
- (b)
- move at a constant acceleration in a straight line.
- (c)
- move in a circle.
- (d)
- gradually slow down due to friction or air resistance.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 29.
- What is always true when an object accelerates?
- (a)
- it speeds up or slows down.
- (b)
- it changes direction.
- (c)
- its mass changes.
- (d)
- a force is acting on it.
- (e)
- its momentum remains constant.
- 30.
- You are in a spacecraft orbiting the Earth and release a
pencil, which floats in front of your face. The pencil is
- (a)
- acted upon by no forces.
- (b)
- too light to be affected by gravity.
- (c)
- moving in a straight line at constant velocity.
- (d)
- accelerating away from the Earth.
- (e)
- accelerating toward the Earth.
- 31.
- The acceleration of gravity on the Moon is about 1/6 of the
acceleration of gravity on the Earth. Compared with your mass on
Earth, your mass on the moon would be
- (a)
- 36 times more.
- (b)
- 6 times more.
- (c)
- 6 times less.
- (d)
- 36 times less.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 32.
- Suppose that a satellite is given a speed 20% larger than
circular velocity. What would be the shape of the trajectory?
- (a)
- circular.
- (b)
- elliptical.
- (c)
- parabolic.
- (d)
- hyperbolic.
- (e)
- straight line.
- 33.
- Assume that Saturn is 10 times as far from the Sun as the
Earth and that it has 100 times the mass of the Earth. The
gravitational force between Saturn and the Sun is
- (a)
- 100 times the force between the Earth and Sun.
- (b)
- 10 times the force between the Earth and Sun.
- (c)
- equal to the force between the Earth and Sun.
- (d)
- one tenth the force between the Earth and Sun.
- (e)
- 1/100 the force between the Earth and Sun.
- 34.
- Which of the following is NOT an action-reaction pair
of forces?
- (a)
- Your weight and the normal force of the floor.
- (b)
- The force ejecting exhaust gases from the back of a rocket
and the force that the exhaust gases exert on the rocket.
- (c)
- Your weight and the gravitational force of you on the Earth.
- (d)
- The force of a car door on you as you speed around a curve
and the force pushing you out.
- (e)
- The tension in a rope holding up an object and the object's
weight.
- 35.
- The tides on Earth due to the Moon are stronger than the
tides due to the Sun because:
- (a)
- the Moon revolves around the Earth faster than the Earth
revolves around the Sun.
- (b)
- the closer distance of the Moon compensates for its smaller
mass.
- (c)
- the tidal acceleration of the Sun must be applied to the
other planets.
- (d)
- the Moon always shows the same face to the Earth.
- (e)
- the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit (around the Earth) is
larger than the eccentricity of the Earth's orbit (around the Sun).
- 36.
- Suppose a source of electromagnetic radiation is moving
away from us at 2% of the speed of light. What can be said of the
wavelength of the waves we receive from the source?
- (a)
- they are redshifted by 2%.
- (b)
- they are blueshifted by 2%.
- (c)
- they are redshifted by 4%.
- (d)
- they are blueshifted by 4%.
- (e)
- there is no change.
- 37.
- Astronomers at Rutgers University are interested in building
an optical telescope for scientific research and are asking your
advice for where to site the telescope. Which of the following is not
likely to be an attribute of a good observing site?
- (a)
- dark sky.
- (b)
- atmospheric stability.
- (c)
- low elevation.
- (d)
- low humidity.
- (e)
- clear sky.
- 38.
- Why do X-ray telescopes have to be placed on space
satellites?
- (a)
- they are too sensitive to terrestrial radiation.
- (b)
- they are too dangerous for astronomers to operate on the
ground.
- (c)
- there is too much scattered sunlight in the Earth's
atmosphere.
- (d)
- the mirrors for X-ray telescopes are too large to operate
on the ground.
- (e)
- the Earth's atmosphere absorbs cosmic X-rays.
- 39.
- Which of the following lists the various bands of the
electromagnetic in order of increasing wavelength?
- (a)
- gamma-rays, X-rays, optical, ultraviolet, radio
- (b)
- radio, infrared, optical, X-ray, gamma-ray
- (c)
- X-rays, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, radio
- (d)
- radio, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, X-ray
- (e)
- gamma-rays, X-rays, optical, ultraviolet, infrared
- 40.
- Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- (a)
- The intensity of electromagnetic radiation decreases with
the square of the distance from a source.
- (b)
- The speed of light is less in glass than it is in vacuum.
- (c)
- The wavelength of a wave is inversely proportional to its
frequency.
- (d)
- Dispersion is the separation of light according to
wavelength.
- (e)
- The index of refraction of air is slightly less than 1.
- 41.
- How many 4 meter telescopes would be required to match the
light gathering power of a 16 meter telescope?
- (a)
- 2
- (b)
- 4
- (c)
- 12
- (d)
- 16
- (e)
- 20
- 42.
- Which of the following telescopes has the best theoretical
resolving power for radiation of wavelength 500 nanometers?
- (a)
- 3 meter aperture and a 3 meter focal length.
- (b)
- 2 meter aperture and a 2 meter focal length.
- (c)
- 2 meter aperture and a 3 meter focal length.
- (d)
- 2 meter aperture and a 4 meter focal length.
- (e)
- 1 meter aperture and a 3 meter focal length.
- 43.
- Reflecting telescopes have many advantages over
refractors. Which of the following is NOT a true advantage?
- (a)
- The primary optical element need be polished on one side only.
- (b)
- A mirror can be supported all across its back.
- (c)
- Light doesn't pass through a mirror, so the glass doesn't
need to be free of internal imperfections.
- (d)
- Some light is absorbed by the primary lens in a refractor.
- (e)
- Reflectors have more light gathering power than refractors
of the same aperture.
- 44.
- The two most abundant elements in the solar system are
- (a)
- Hydrogen and Helium
- (b)
- Hydrogen and Iron
- (c)
- Iron and Nickel
- (d)
- Silicon and Oxygen
- (e)
- Oxygen and Carbon
- 45.
- If the temperature of the Sun were to decrease while its
size remained the same, it would become
- (a)
- bluer and brighter.
- (b)
- bluer and fainter.
- (c)
- redder and brighter.
- (d)
- redder and fainter.
- (e)
- there would be no change.
- 46.
- The temperature of the Sun is 6000 K and the Sun's radiation
is brightest at a wavelength of about 5000 Å. The temperature of
Mercury's sunlit side is about 600 K. At what wavelength is Mercury's
radiation brightest?
- (a)
- 500 Å.
- (b)
- 5000 Å.
- (c)
- 6000 Å.
- (d)
- 50,000 Å.
- (e)
- none of the other answers is correct.
- 47.
- Suppose a number of planets all have the same mass, but
different sizes and temperatures. Which of the following would be
most likely to retain a thick atmosphere?
- (a)
- a small, hot planet.
- (b)
- a small, cool planet.
- (c)
- a large, hot planet.
- (d)
- a large, cool planet.
- (e)
- a cool planet of any size.
- 48.
- Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- (a)
- The pressure at sea level on the Earth is produced by the
weight of the entire overlying atmosphere.
- (b)
- The Earth and Venus are able to retain nitrogen and oxygen,
but not hydrogen, in their atmospheres.
- (c)
- Higher temperature gases contain molecules that tend to
move with higher speeds.
- (d)
- When the density of a gas is increased at constant
pressure, its temperature decreases.
- (e)
- The molecules of a gas like oxygen tend to move with higher
speeds than the molecules of a gas like hydrogen, all other things
(like pressure, temperature, etc.) being equal.
- 49.
- If the half-life of a radioactive isotope is
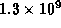 years, how much of the original amount will be left after
years, how much of the original amount will be left after
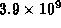 years?
years?
- (a)
- one quarter
- (b)
- one third
- (c)
- one eighth
- (d)
- one half
- (e)
- one sixteenth
- 50.
- Radioactive heating of the planets has been
- (a)
- gradually decreasing since the formation of the solar system.
- (b)
- gradually increasing since the formation of the solar system.
- (c)
- constant since the formation of the solar system.
- (d)
- an unimportant source of heat energy.
- (e)
- the only source of heat energy, other than solar radiation.



Next: About this document
John Hughes
Tue Oct 20 15:34:48 EDT 1998
 , altitude 0
, altitude 0 
 , altitude 90
, altitude 90 
 , altitude 0
, altitude 0 
 , altitude 180
, altitude 180 
 , altitude 90
, altitude 90 
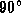 from the zenith.
from the zenith.